10 Reasons Why Electric Cars Are Bad For The Environment: Expert Analysis

Electric cars are often hailed as the future of eco-friendly transportation. However, there are hidden downsides that many people overlook. In this article, we’ll uncover 10 reasons why electric cars are bad for the environment, challenging the common perception of them being the ultimate green solution.
The Hidden Environmental Impact of Battery Production
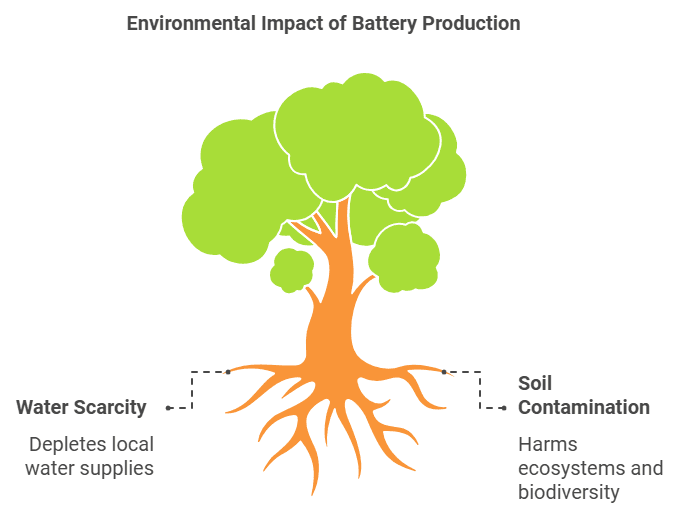
Manufacturing lithium-ion batteries for electric cars requires substantial energy and resources. The extraction of lithium and other rare earth metals consumes large amounts of water and energy, often resulting in significant environmental degradation. For instance:
- Water Scarcity: Lithium mining in arid regions leads to the depletion of local water supplies, affecting agriculture and community access to water.
- Soil Contamination: Mining operations can release toxic chemicals into the soil, harming local ecosystems and biodiversity.
The environmental impact of battery production can’t be ignored when assessing the true eco-friendliness of electric vehicles.
Electric Cars and Fossil Fuels: A Negative Connection
While electric cars don’t emit tailpipe emissions, the electricity they use often comes from fossil fuel power plants. In countries where coal is a primary energy source, charging an electric car can result in higher overall carbon emissions than driving a fuel-efficient internal combustion engine vehicle. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration:
- 60% of electricity in the United States was generated from fossil fuels in 2021.
- Coal and natural gas are major contributors to electricity generation.
This reliance on non-renewable energy sources highlights one of the significant negatives of electric cars that is frequently overlooked.
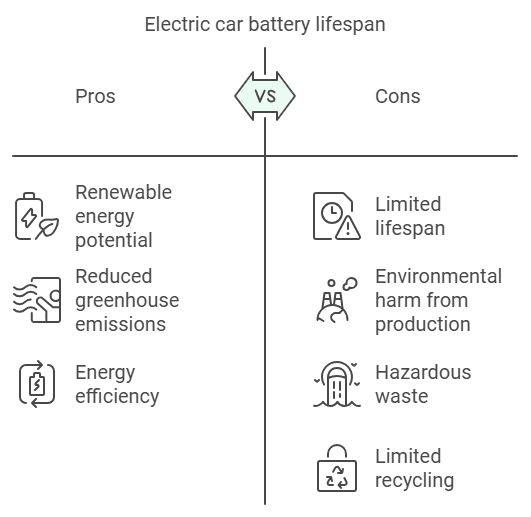
The Downsides of Electric Car Battery Lifespan
Electric car batteries have a limited lifespan, typically requiring replacement after 8-10 years. Producing new batteries contributes to additional environmental harm, and disposing of old batteries poses significant ecological challenges:
- Hazardous Waste: Improper disposal can lead to soil and water pollution due to toxic substances like lead and acid.
- Limited Recycling: Current recycling technologies are not widely implemented, leading to accumulation of battery waste.
The downside of electric cars includes dealing with hazardous waste from battery disposal, which can lead to long-term environmental issues.
As with any car, electric vehicles require maintenance. For instance, learning how to remove water spots from your car can help preserve its exterior.
Bad Things About Electric Cars: The Cost of Rare Earth Minerals
The production of electric motors and batteries requires rare earth minerals such as cobalt and nickel. Mining these materials is often associated with:
- Unethical Practices: Poor working conditions and child labor in countries lacking strict regulations.
- Environmental Damage: Deforestation, water contamination, and loss of biodiversity due to mining activities.
This exploitation is one of the bad things about electric cars that consumers rarely hear about.
The complexities of electric car components don’t stop at the batteries. Understanding how to wrap a car for beginners can be useful for those looking to protect their vehicle’s finish.
Issues with Electric Vehicles: Charging Infrastructure Concerns
Electric vehicles require a widespread charging infrastructure, which is still lacking in many regions. Building new charging stations involves:
- Resource Consumption: Production and installation require materials and energy, adding to the carbon footprint.
- Environmental Impact: Construction can lead to habitat disruption and increased emissions.
Unlike gas stations, electric charging stations are not yet ubiquitous, making long-distance travel a challenge for electric vehicle owners. These infrastructure challenges are among the significant issues with electric vehicles.
If you’re considering transportation options, you might find our guide on car rental companies in Europe helpful for understanding alternative solutions.
Electric Car Production: An Environmental Burden
Manufacturing electric cars demands more energy than producing conventional cars due to the complexity of their components, particularly the batteries. This high energy consumption leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions during the production phase. For example:
- Higher Emissions: A study in the Journal of Industrial Ecology found that producing electric car batteries emits over twice as much CO₂ as producing traditional cars.
- Energy Sources: If manufacturing plants use fossil fuels, the environmental burden is even greater.
The environmental impact of electric car production often outweighs the benefits achieved during the vehicle’s operational life.
The Environmental Impact of Battery Disposal
Disposing of used electric car batteries poses a significant environmental challenge. The chemicals and heavy metals in lithium-ion batteries can leach into the soil and water systems if not properly recycled or disposed of:
- Soil and Water Pollution: Toxic substances can contaminate ecosystems, affecting wildlife and human health.
- Limited Recycling Infrastructure: Many countries lack the facilities to handle large-scale battery recycling.
These factors contribute to the 10 reasons why electric cars are bad for the environment, and battery disposal plays a significant role.
To ensure your vehicle remains efficient, regular maintenance is key. Our ultimate vehicle maintenance log templates can help you keep track of your car care routine.
Electric Cars and the Strain on Power Grids
The increasing number of electric vehicles can strain existing power grids, especially during peak charging times. This strain may lead to:
- Increased Fossil Fuel Use: Backup power plants, often fossil fuel-based, may be needed to meet demand.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Upgrading grids requires significant resources and can have its own environmental impacts.
Charging times for electric cars can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the battery technology and charger type. This variability adds stress to power systems not designed for such demands.
Downsides of Electric Cars Using Non-Renewable Energy
In many areas, the electricity used to charge electric cars comes from non-renewable sources like coal and natural gas. This means that even though electric cars have zero tailpipe emissions, they indirectly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions:
- Carbon Footprint: The overall emissions depend on the energy mix of the grid.
- Renewable Energy Availability: Limited access to solar panels and wind energy in some regions.
Until there is a complete shift to renewable energy sources, the downsides of electric cars in terms of environmental impact remain substantial.
Alternatively, students might benefit from our article on student car rental when looking for cost-effective transportation methods.
Negatives of Electric Cars: The Tailpipe Emissions Myth
While electric cars produce no tailpipe emissions, this doesn’t mean they are entirely emission-free. The manufacturing process, battery production, and electricity generation all contribute to their overall carbon footprint:
- Lifecycle Emissions: Total emissions can sometimes be comparable to efficient gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Emission Shifting: Pollution is shifted from the vehicle to the power plants and manufacturing facilities.
Comparatively, modern gasoline-powered vehicles have significantly reduced emissions due to better fuel efficiency and cleaner fuel formulations.

Conclusion
Electric cars present a complex picture when it comes to environmental impact. While they offer advantages in reducing tailpipe emissions, there are significant hidden costs associated with their production, energy sources, and battery disposal. Understanding these 10 reasons why electric cars are bad for the environment can help consumers make more informed decisions. It’s essential to consider the full lifecycle of electric vehicles and advocate for renewable energy sources and improved recycling technologies.
What’s your take on the environmental impact of electric cars? Join the conversation and share your thoughts below!







